The Classification for the MeteoLaser LiDAR from UL International GmbH according to IEC 61400-12-1 ed.2 (2017), Annex L is now available.
Object of an IEC classification
In order to obtain a classification a minimum of three measurement campaigns of at least two devices for at least two locations have to be performed.
The object of a classification is to identify and quantify sensitivities on the measurement accuracy uncertainty arising from various environmental parameters.
The environmental variables that have been analyzed are:
- wind shear
- turbulence intensity
- rain
- availability
- wind direction
- air temperature
- air density
- temperature gradient
- upflow angle
- wind veer.
Sensibility to environmental parameters
The classification has shown that wind shear and turbulence intensity are the environmental parameters with the biggest impact on the accuracy uncertainty (same as for other pulsed LiDAR).
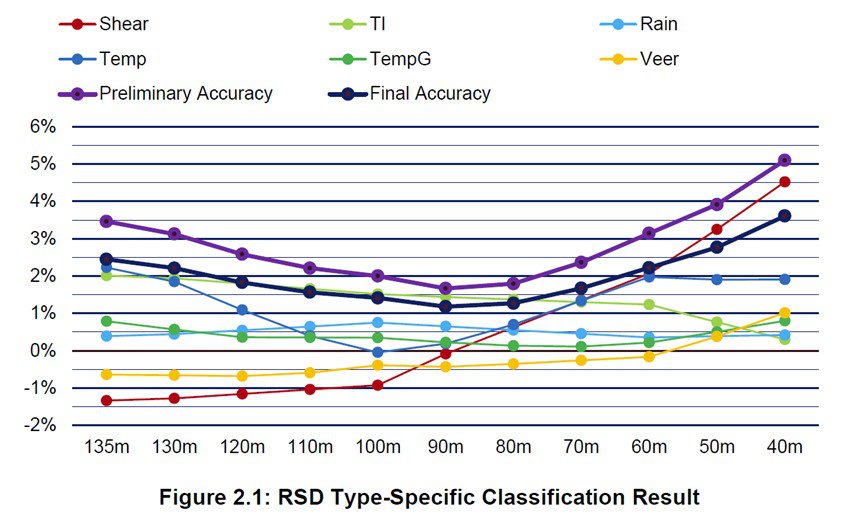
Classification results
The result of the classification is the Final Accuracy Class, which is linked to the standard measurement uncertainty (standard uncertainty= Final accuracy class/√3).
MeteoLaser
| Height (m) | Preliminary accuracy | Final Accuracy Class | Standard Uncertainty in % |
| 135 m | 3,46% | 2,45% | 1,41% |
| 120 m | 2,58% | 1,83% | 1,05% |
| 100 m | 2,00% | 1,41% | 0,82% |
| 80 m | 1,79% | 1,27% | 0,73% |
| 60 m | 3,14% | 2,22% | 1,28% |
Extract from table 2.11: RSD type-specific Classification for selected heights
We see very good results with low measurement uncertainties.
The final Accuracy Classes are in the range of 1,27% to 2,45%, in Line with what you can expect from a high-end pulsed LiDAR.

